Kidney Cancer
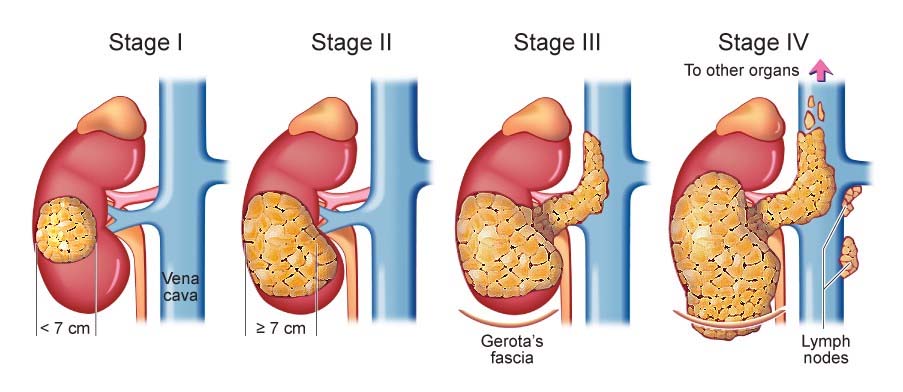
Kidney Cancer is an out-of-control, abnormal growth of cells in the kidney. Basically, several types of cancer begin from kidney, but the most popular are renal cell cancer and
transitional cell carcinoma. Both these cancers begin from the inner lining of the cancer. It is extremely important to understand the type of cancer because the treatment,
staging and prognosis is different for each type.
Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
- 1. Instant weight loss
- 2. Loss of appetite
- 3. High temperature
- 4. Swelling in leg and ankle
- 5. High blood pressure
- 6. Occurrence of blood in urine
- 7. Lower Back Pain
- 9. Occurrence of lumps in abdomen
1.Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts when cells that make up the urinary bladder start to grow out of control.
As more cancer cells develop, they can form a tumor and, with time, spread to other parts of the body.
Different types of cells in your bladder can become cancerous. The type of bladder cell where cancer begins determines the type of bladder cancer.
The type of bladder cancer determines which treatments may work best for you.
1. Urothelial Carcinoma.Urothelial carcinoma, previously called transitional cell carcinoma, occurs in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
Urothelial cells expand when your bladder is full and contract when your bladder is empty. These same cells line the inside of the ureters and the urethra,
and tumors can form in those places as well. Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States
2.Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder, for instance from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter.
Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States. It's more common in parts of the world where a certain parasitic infection (schistosomiasis) is a common cause of bladder infections.
3. Adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma begins in cells that make up mucus-secreting glands in the bladder. Adenocarcinoma of the bladder is rare in the United States
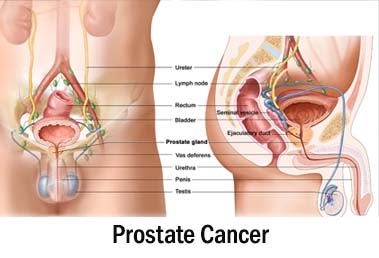
2.Prostate Cancer
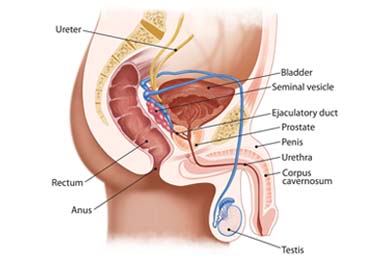
The prostate is a small gland about the size of a walnut. The prostate gets bigger as men get older. It is divided into 2 lobes and has an outer layer called the capsule.
The prostate is below the bladder surrounding the first part of a tube called the urethra. The urethra carries pee (urine) from the bladder to the penis. The same tube also carries semen, which is the fluid containing sperm. Just behind the prostate is the back passage (rectum).
Symptoms
Prostate cancer may cause no signs or symptoms in its early stages
Prostate cancer that's more advanced may cause signs and symptoms such as:
- • Decreased force in the stream of urine.
- • Blood in semen.
-
- • Discomfort in the pelvic area.
-
- • Bone pain.
-
- • Erectile dysfunction.
-